Yemen has been the scene of complex conflicts and political upheavals. At the heart of this tumult are the Houthis, a rebel group that has emerged as a major player on the Yemeni political scene.

Today, the Houthis control a large part of Yemeni territory, including the major port of Hodeïda. Their economic and military power enables them to keep the internationally recognized government at bay.
Who are the Houthis?
The Houthis are a political and religious movement from northern Yemen, in the Saada region. Founded in the late 1990s by Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, the movement takes its name from the Houthi family. They still play a central role in the movement’s decision-making. Initially, the Houthis were a Zaydi movement, a branch of Shiism. They subsequently evolved into a political and military force capable of competing with the government.
Their rise to power has been fueled by a mixture of political, economic and religious grievances. Indeed, the Houthis opposed the political and economic marginalization of Yemen’s northern regions. They criticized the central government for its corruption and alignment with foreign powers, notably Saudi Arabia and the United States.
Houthi ideology
Their ideology is imbued with strong anti-imperialist and anti-American sentiment, as well as fervent Yemeni nationalism. The Houthis have also adopted a religious discourse, presenting themselves as defenders of the interests of the Zaydites and the oppressed against outside forces and corrupt elites.
The Houthis belong to the Zaydi branch of Shi’ism, one of the main schools of thought in Shi’ite Islam. Zaydism is widespread mainly in Yemen, where it makes up the majority of the population in the northern regions.
This branch of Shi’ism is distinguished by its interpretation of the succession of the Prophet Muhammad and its emphasis on social and political justice. The Zaydites believe that an Imam descended directly from the Prophet Muhammad should lead the Muslim community. He must be chosen on the basis of merit and piety, rather than dynastic lineage.
Although the Houthis are strongly rooted in the Zaydi tradition, their discourse and actions go far beyond religious issues to encompass broader political and social concerns.
Abd el Malek Al Houthi, the charismatic leader of the Houthis, embodies this fusion of religiosity and political commitment. His followers revere him as both a religious leader and a political guide. He unites the two dimensions of authority in the Zaydi tradition. His speeches are imbued with religious references and Koranic verses. They reinforce his status as a spiritual leader while articulating a political vision for Yemen.
The Houthis in a position of strength in Yemen
Yemen has been in the grip of civil war since 2014. The Houthis took control of the capital, Sanaa, in 2014. They overthrew the Saudi-backed government and forced the Yemeni president, Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, into exile. Since then, Yemen has been plunged into a violent and devastating conflict, exacerbated by the military intervention of the coalition led by Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates in support of Hadi’s government.
The Houthis have succeeded in resisting the Arab coalition’s offensives and consolidating their hold on large swathes of Yemeni territory, including Sana’a and other key regions. Their stubborn resistance and ability to mobilize broad popular support have enabled them to remain a key political player despite international pressure and coalition attempts to oust them from power.
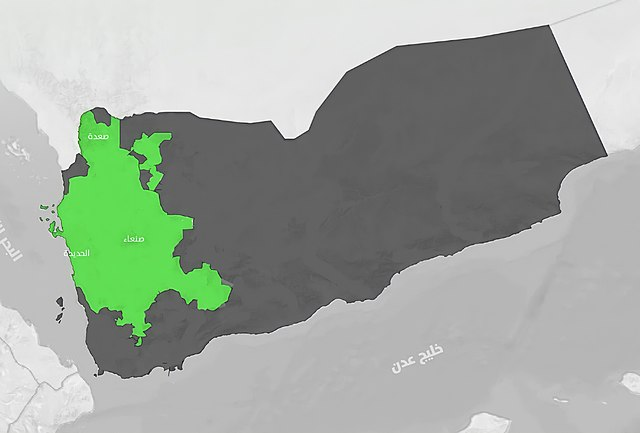
Today, they have considerable military power. The Houthis are not a rag-tag rebellion. On the contrary, they have taken over the resources, weapons and know-how of the regular army in the areas they control. Some of the military personnel who served the regime have been transferred to the Houthis as part of their territorial conquests. They simply need to feed their families. Today, the Houthis are capable of producing and deploying sophisticated weaponry. What’s more, they benefit from the support of Iran. The port of Hodeïda also provides them with substantial revenue. This enables them to sustain their war effort.
*
The Houthis continue to play a central role in Yemeni politics, defying the expectations and forecasts of many international observers. Their meteoric rise and resilience in the face of external pressures testify to the complexity and depth of the political and social dynamics shaping the contemporary Yemeni landscape.
